What Is A Physical Map Of A Chromosome A physical map as related to genomics is a graphical representation of physical locations of landmarks or markers such as genes variants and other DNA sequences of interest within a chromosome or
Gene mapping or genome mapping describes the methods used to identify the location of a gene on a chromosome and the distances between genes Gene mapping can also describe the distances between different sites within a gene The essence of all genome mapping is to place a collection of molecular markers onto their respective positions on the genome Molecular markers come in all forms Genes can be viewe Low resolution physical mapping is typically capable of resolving DNA ranging from one base pair to several mega bases In this category most mapping methods involve generating a somatic cell hybrid panel which is able to map any human DNA sequences the gene of interest to specific chromosomes of animal cells such as those of mice and hamsters The hybrid cell panel is produced by collecting hybrid cell lines containing human chromosomes identified by polymerase chain reaction
What Is A Physical Map Of A Chromosome

What Is A Physical Map Of A Chromosome
https://fr.maps-mexico-mx.com/img/0/mexicaine-carte.jpg
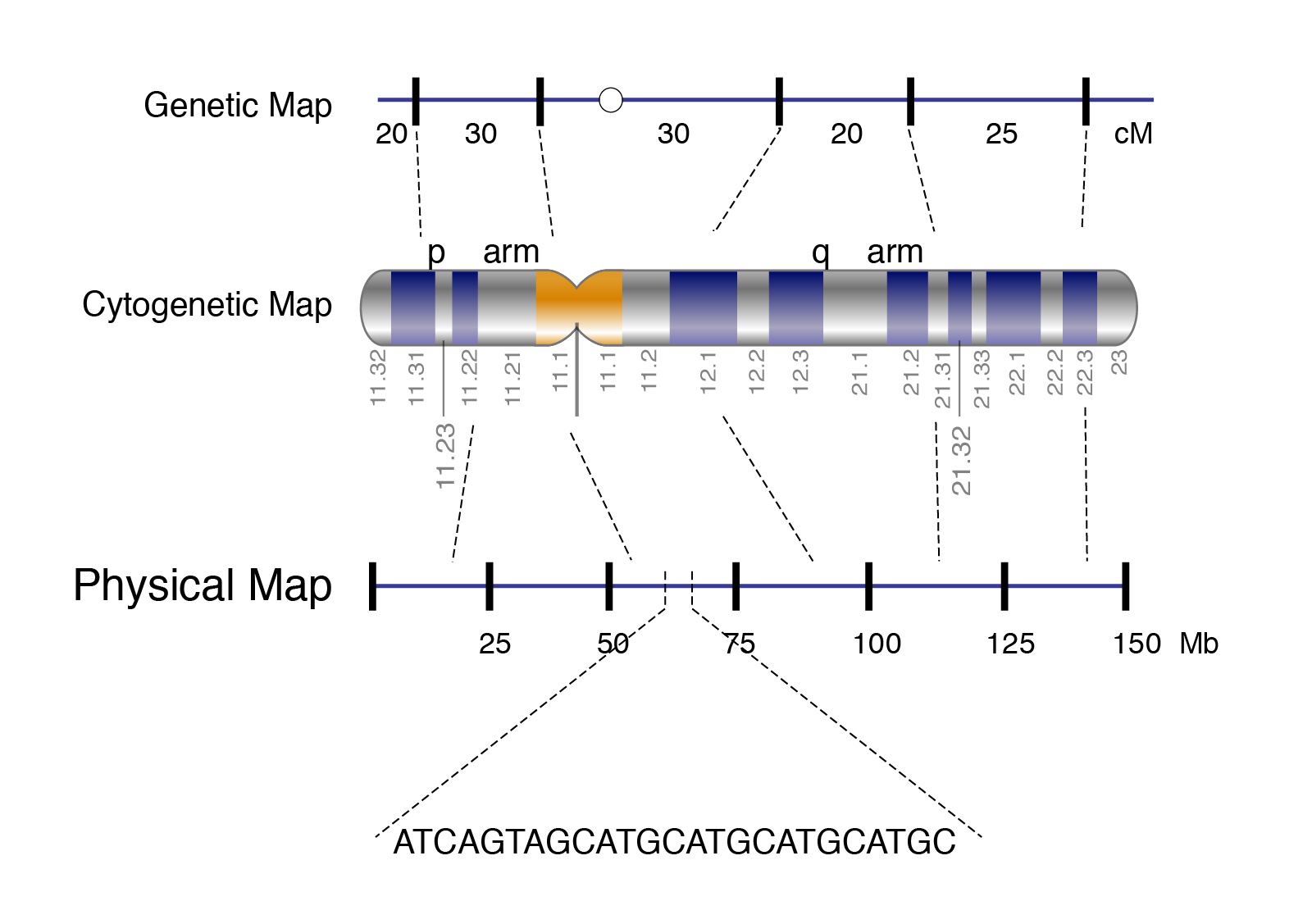
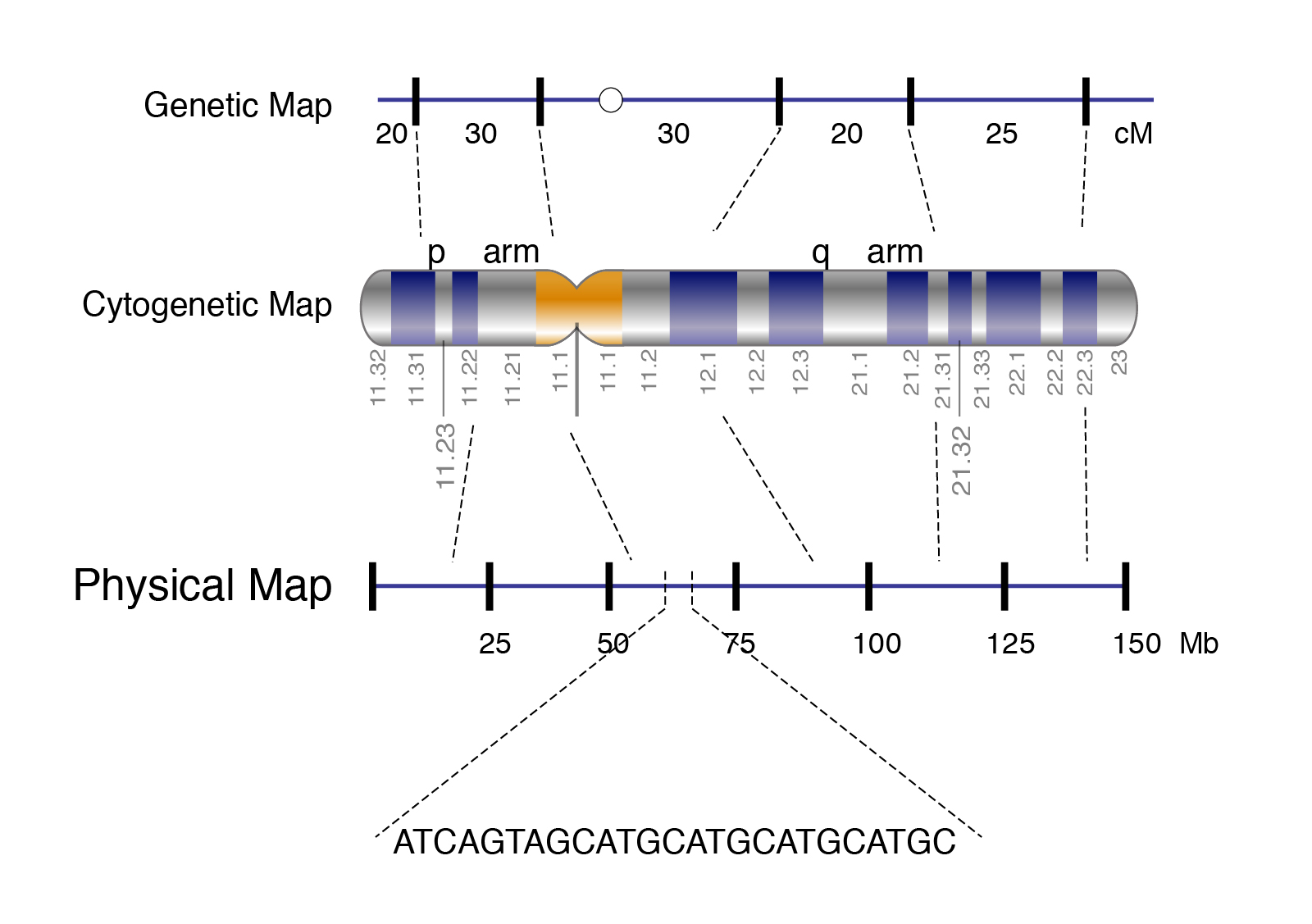
Physical Map
https://www.genome.gov/sites/default/files/tg/en/illustration/physical_map.jpg

Physical Maps
http://www.vidiani.com/maps/maps_of_north_america/physical_map_of_north_america.jpg
To create a physical map large fragments of the genome are cloned into plasmid vectors or into larger vectors called bacterial artificial chromosomes BACs BACs can contain approximately 100kb fragments A physical map provides detail of the actual physical distance between genetic markers as well as the number of nucleotides There are three methods used to create a physical map cytogenetic mapping radiation hybrid mapping and
Physical maps specify the distances between landmarks along a chromosome Ideally the distances are measured in nucleotides so that the map provides a direct description of a chromosomal DNA molecule The most important A physical map provides detail of the actual physical distance between genetic markers as well as the number of nucleotides There are three methods used to create a physical map cytogenetic mapping radiation hybrid
More picture related to What Is A Physical Map Of A Chromosome

What Is Physical Hazard Astonishingceiyrs
https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018311491_1-d57d450e11519fbb7c75675932785012.png
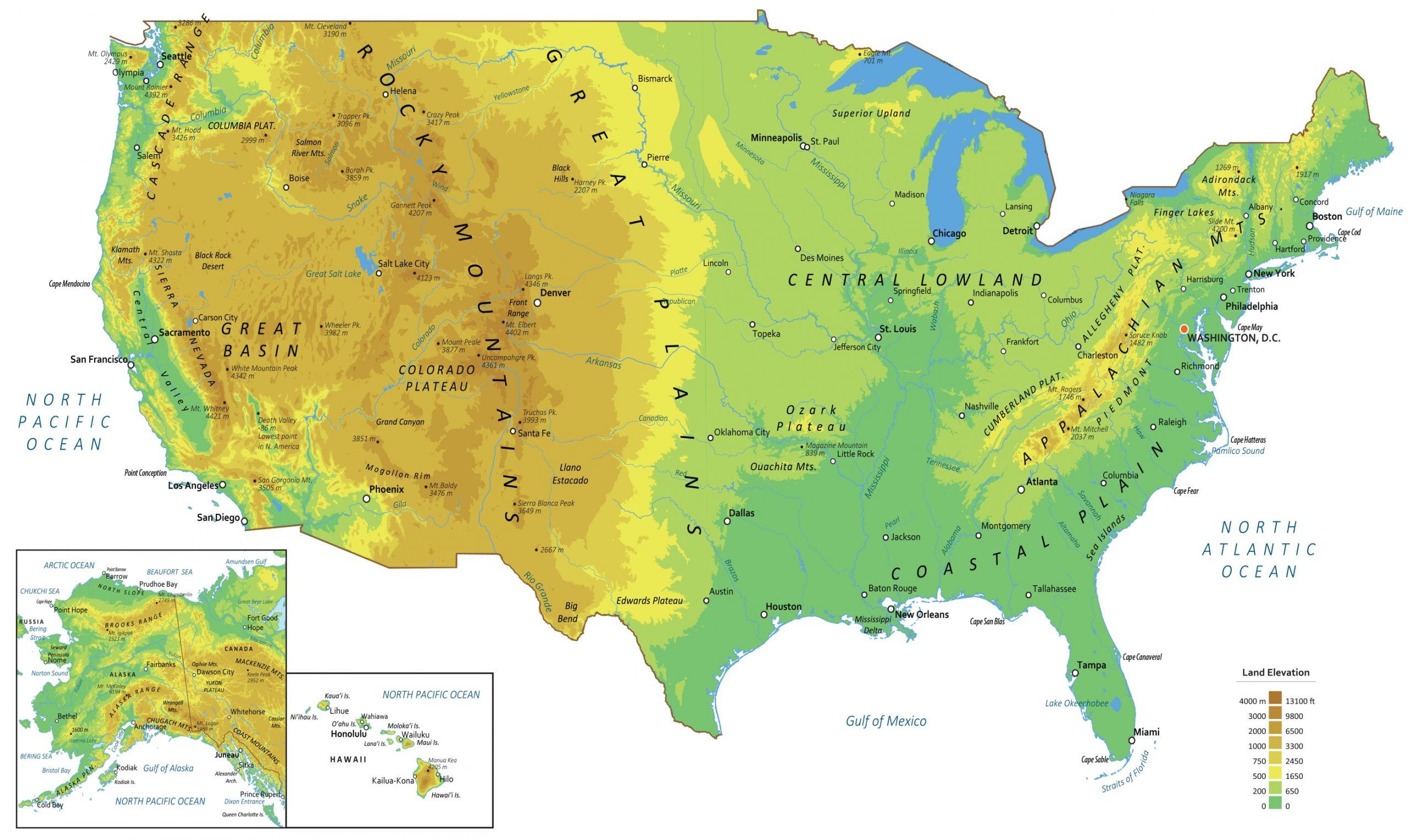
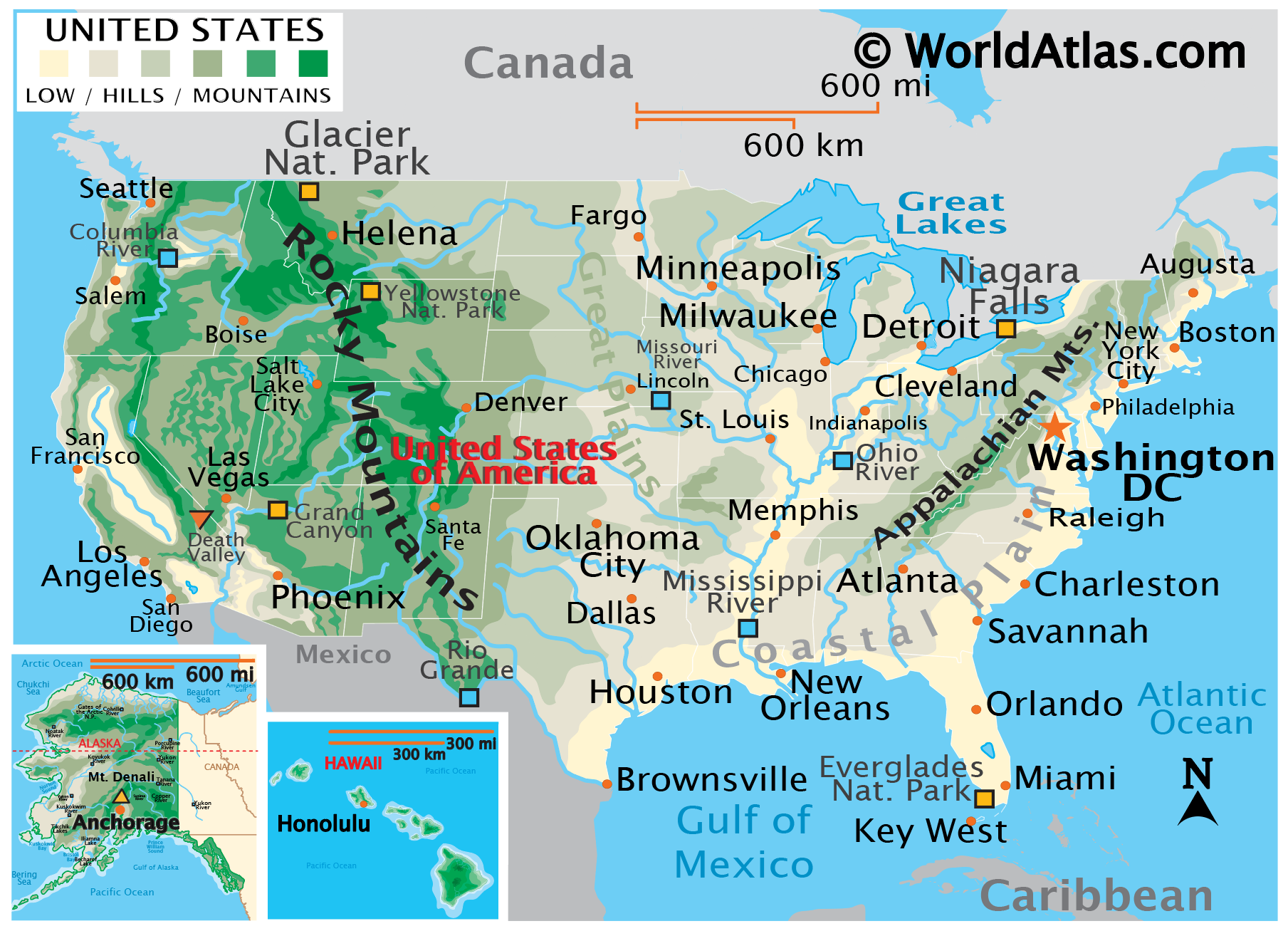
United States Map Geographical
https://gisgeography.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/US-Physical-Map-scaled.jpg

Important Features Of Map Connie Celestina
https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20230605134022/Physical-Features-of-India-660.png
Physical Mapping in Organisms A novel physical mapping approach has been developed that refines the positions of sex determining genes on specific chromosomes This method is adaptable and can be applied to In a physical map gene are depicted in the same order as they occur in chromosomes and the distances between them are shown as number of base pair separating the genes For example genes sc and w of Drosophila
A physical map orders genes or markers along the DNA strand of a chromosome Finally a DNA sequence strung together is the most precise type of map in that it contains both coding A genetic map shows the relative positions of genes on a chromosome based on recombination frequencies while a physical map shows the actual physical distances between
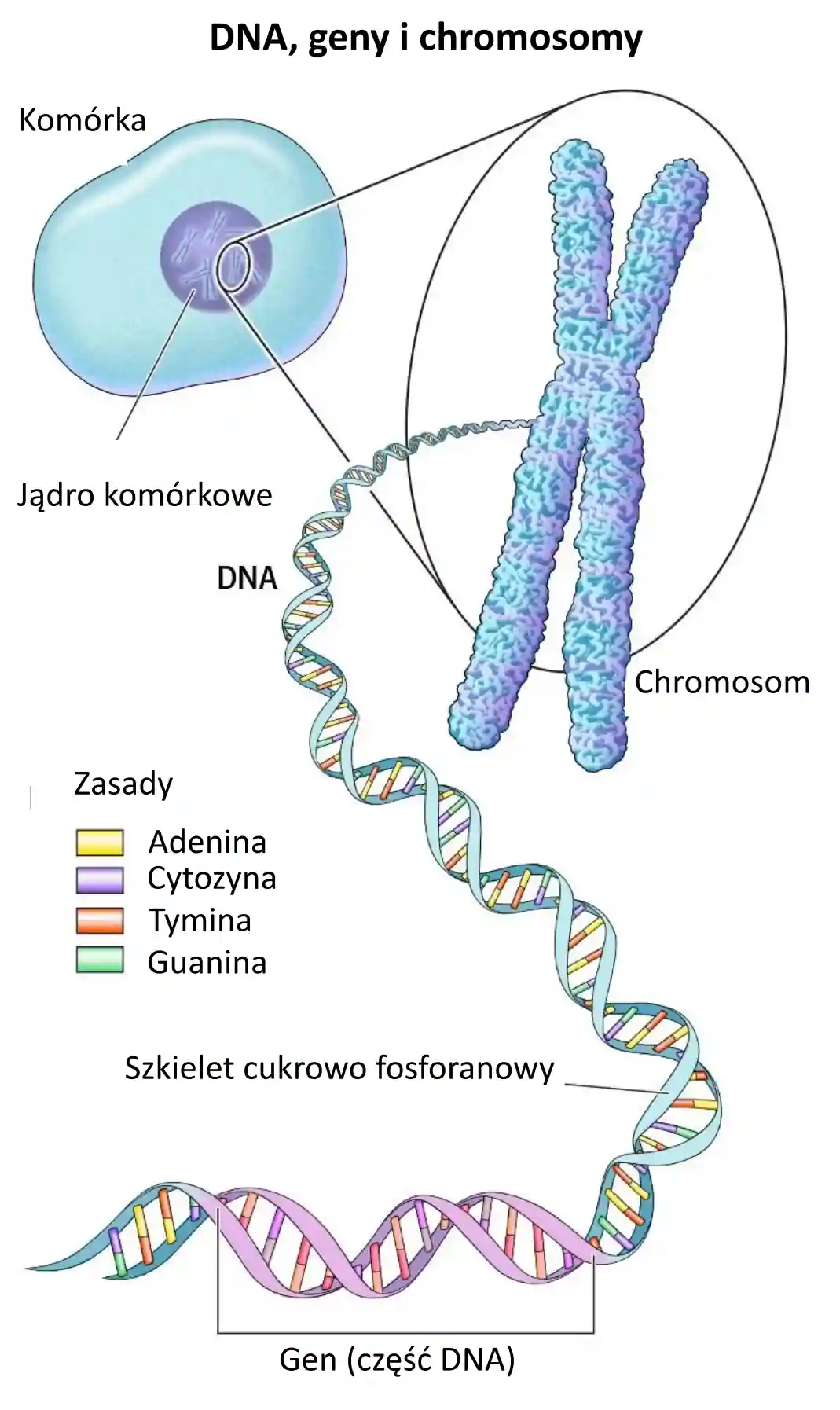
Podstawy Genetyki StopDuchenne Poland
https://stopduchenne.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/DNA-genes-chromosomes-webp-jakosc-20-1.webp
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-physical-therapy-7481022-Horiz-V2-c694fce273e14ddf9c02103a045e1454.jpg)
Physical Therapy Why You Need It And What To Expect
https://www.health.com/thmb/a86BAN60XANZoNvVYGQSPh2bDyQ=/1500x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-physical-therapy-7481022-Horiz-V2-c694fce273e14ddf9c02103a045e1454.jpg

https://www.genome.gov › genetics-glossa…
A physical map as related to genomics is a graphical representation of physical locations of landmarks or markers such as genes variants and other DNA sequences of interest within a chromosome or
https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Gene_mapping
Gene mapping or genome mapping describes the methods used to identify the location of a gene on a chromosome and the distances between genes Gene mapping can also describe the distances between different sites within a gene The essence of all genome mapping is to place a collection of molecular markers onto their respective positions on the genome Molecular markers come in all forms Genes can be viewe

Culture Trait Examples

Podstawy Genetyki StopDuchenne Poland
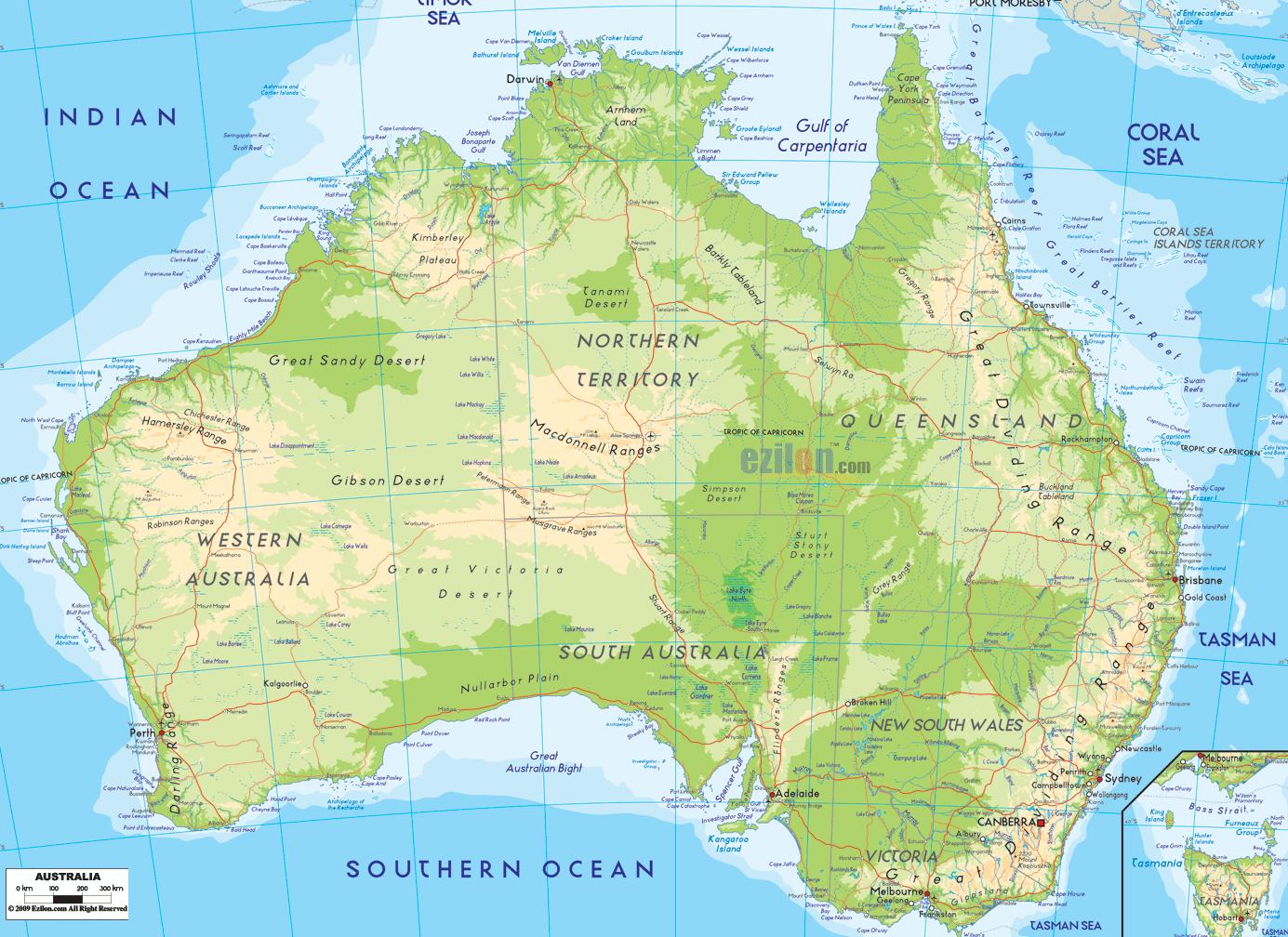
Australi Fysieke Kaart Een Fysieke Kaart Van Australi Australi En
Advanced Agriculture GIS Applications GIS

Beneficios Del Ejercicio Para Su Salud F sica Y Mental National

Africa Physical Features Slides Geography Docsity

Africa Physical Features Slides Geography Docsity

CH 4 U S Canada Physical FLASHCARDS MAP Diagram Quizlet
VIRTUAL CHAN Physiographic Regions Of Canada Glog

Maps Of The World
What Is A Physical Map Of A Chromosome - Physical maps specify the distances between landmarks along a chromosome Ideally the distances are measured in nucleotides so that the map provides a direct description of a chromosomal DNA molecule The most important